What is Topology?
Topology is the wireframe or mesh of a 3D object. This mesh is made up of many simple geometric shapes and each shape is referred to as a face. This is where different types of topology, different shapes used for the wireframe, comes in.
There are 3 types of topology:
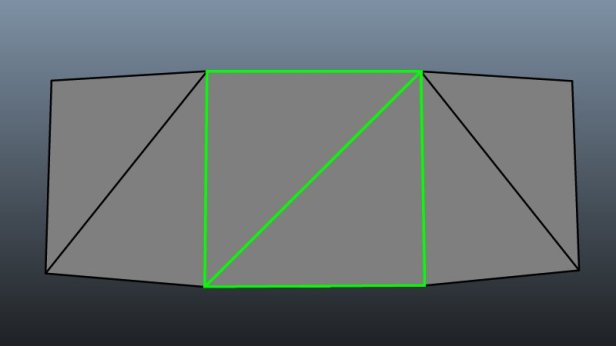
Tris is a topology that uses triangles. Whilst it might be useful for simple models and leave you with a smaller file size, this type of topology is often avoided as when attempting to produce complex meshes, triangles cause problems when subdividing the geometry to increase the resolution of the shape. They’re also difficult to work with when deforming or animating meshes.
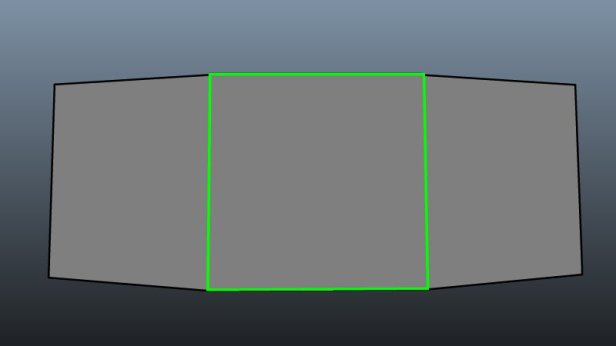
Quads are a topology that uses 4-sided shapes like squares and rectangles. This form of topology is best for creating 3D models as quads ensure that the mesh has clean topology that can deform satisfactorily when animated. Using this kind can be quite a time-consuming method, however.
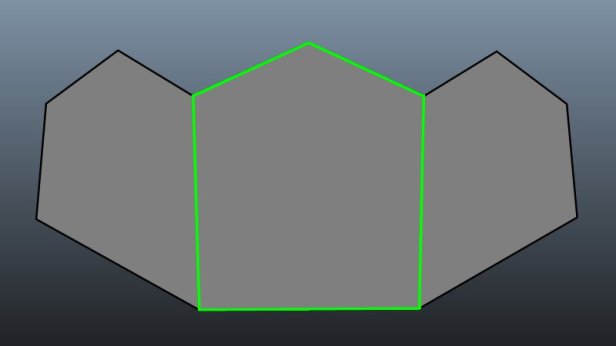
N-Gons are a topology that uses shapes with 5 or more sides. Whilst they are quicker to work and model with, these should always be avoided whenever possible within 3D modelling as they pose to be problematic when texturing, rendering and deforming shapes.
There are 3 points that are used together to make a 3D polygonal wireframe.
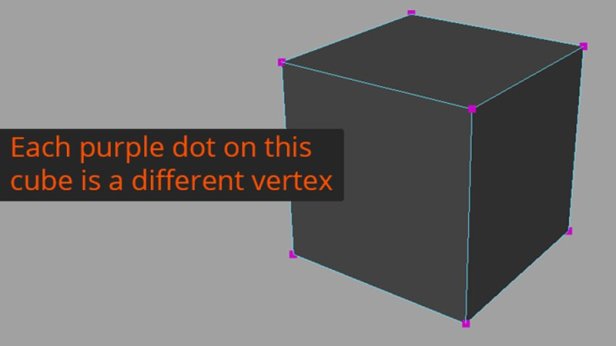
Vertices are the point at which 3 or more edges meet.
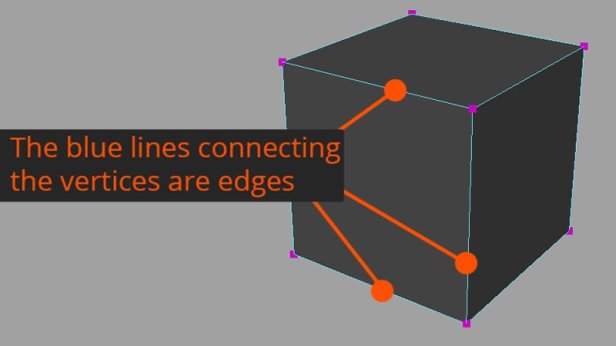
Edges are lines that can be made up of two vertices, arcs or curves.
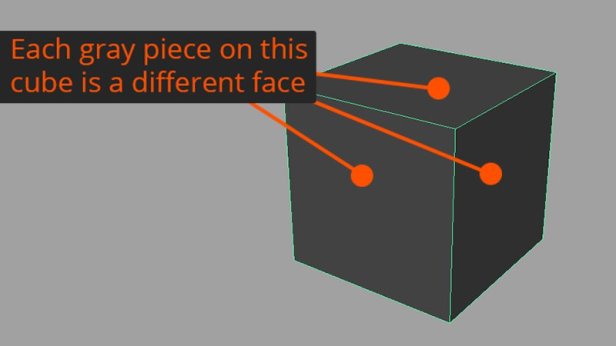
These two features are what forms a face in wireframe design.
Good & Bad Topology
A model with good topology will be able to move in a realistic manner with attention to detail concerning how the model moves. For successful topology these properties must be considered:
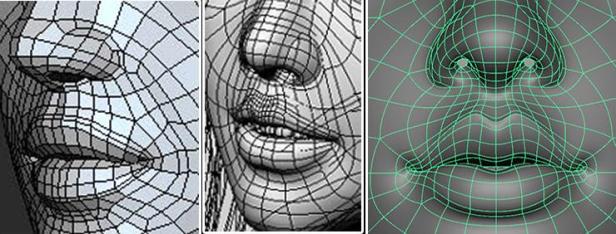
Flow relativity refers to the idea that the spaces between vertices should increase and decrease appropriately to the model’s movement.
Contour proximity refers to the idea that the edges should follow the shape to maintain its relativity.
Variable Density refers to the idea that the density of topology in areas should depend on the curvature and motion of a model. Where there will be a lot of movement or any curvature, the topology should be denser.
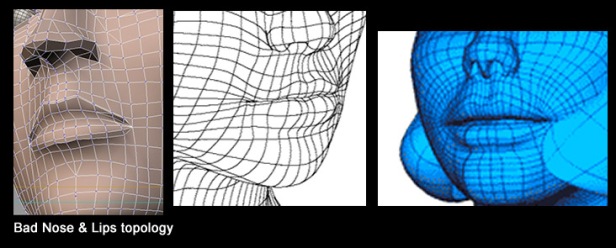
Poor topology will have use of unnecessarily dense mesh in areas with a bad application of flow relativity and a lack of contour proximity. You can get away with using tris topology rather than quad topology when you are able to achieve the same level of quality in less time when using either type. Whilst this can be seen as bad topology, it can also save a lot of time. This will depend on the type of shapes that you’re modelling, however. If you are modelling shapes consisting of only flat planes, you wouldn’t have to use quads as you can get the same results from using tris in this case.
Polygonal Modelling
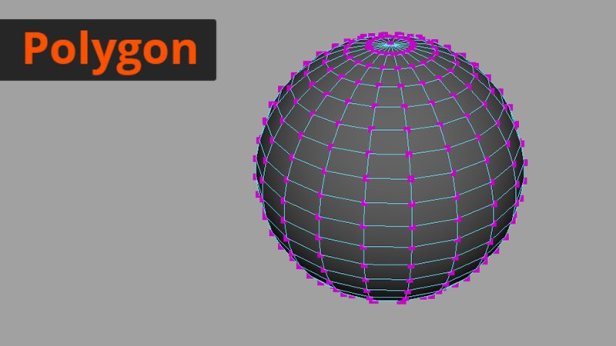
Polygons are often used the most when modelling in 3D. They can be used for all types of objects and so are very versatile but when it comes to creating very smooth surfaces, you would need to use a lot of geometry which could make it more confusing to navigate about your modelled object.
NURBS Based Modelling
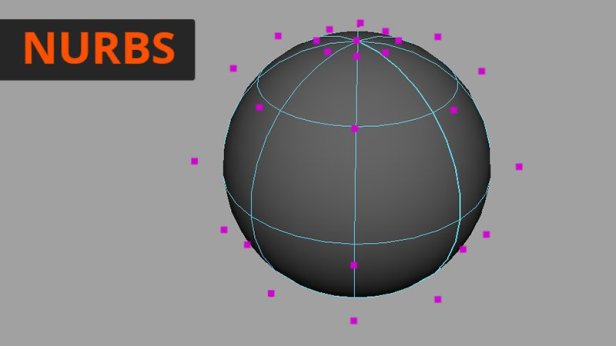
NURBS stands for non-uniform rational b-spline. They are most often used when modelling very smooth objects as they don’t need to use as many points as polygonal geometry would to look smooth. NURBS geometry has four sides that are defined by control points
Subdivisional Modelling
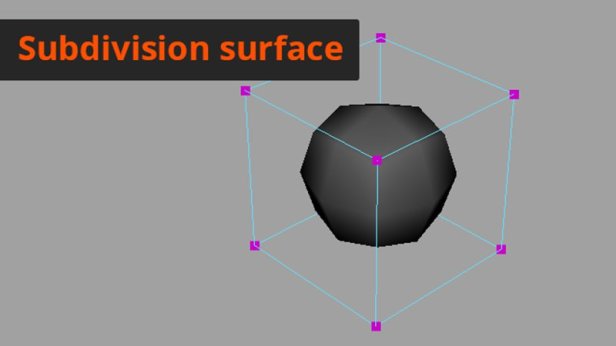
Subdivision modelling, also known as NURMS (non-uniform rational mesh smooth), is similar to polygonal geometry. It takes the polygonal geometry and uses an algorithm to smooth it automatically. This type of modelling is something like a mixture of polygonal and NURB based modelling.
Two-manifold & Non-manifold Topology
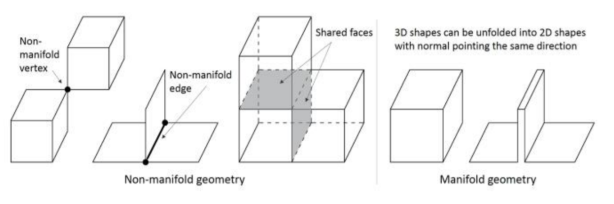
Polygons with two-manifold topology are shapes that can be split along its edges and folded out so that the mesh lays flat without any overlapping pieces – like a net of a 3D shape.

Polygons with non-manifold topology have an arrangement that makes it so that it cannot be unfolded into a flat net-like form and some tools in software like Maya won’t work with these shapes. The images above feature what two manifold geometry should look like and the 3 types of non-manifold geometry.
